Author: Bhushan Joshi, Ericsson Head of Sustainability & Corporate Responsibility for the United States and Canada
The world is waking up to the need to accelerate decarbonization efforts to avoid the worst impact of climate change – the themes of the recent COP27 UN climate talks has been about world leaders urging each other to move faster to cut pollution, while urging greater transparency and accountability from corporations. The ICT industry has a key role to play in enabling global decarbonization efforts by building energy-efficient 5G networks today and collaborating to create a sustainable 6G-enabled future.
As Ericsson’s Head of Sustainability & Corporate Responsibility for the United States and Canada, I collaborate with industry partners to deploy climate action solutions and accelerate the transition of the ICT industry towards achieving Net Zero emissions. One way we do this is through our Breaking the Energy Curve framework, which helps our partners think through a holistic way to reduce energy consumption across network rollouts.
Another example is my participation representing Ericsson in the Next G Alliance’s Green G working group, which is chartered to define a path for the North American ICT industry toward a sustainable future enabled by 6G.
I was recently elected as chair of the Green G working group along with 230 delegates representing a wide range of industry stakeholders. Apart from contributing extensively, I have benefitted from the opportunity to listen to the complementary and supportive perspectives and insights provided by the other members of the working group. All of us share a strong desire for our industry to do its part toward achieving Net Zero carbon emissions.
The path to breaking the energy curve
The starting point for the working group’s first white paper, Green G: The Path Toward Sustainable 6G, is a testament to our progress. Over the course of the last decade, the ICT industry as a whole – including mobile infrastructure, radio access technology, data centers and device manufacturers – has made significant improvements in terms of reducing the overall energy consumption per compute and network traffic. We have a strong foundation to build on.
Since the introduction of 4G, data traffic has grown exponentially, with a 300-fold increase. This traffic growth was initially driven by an increase in the number of subscribers and increased population coverage and is now accelerating with the numbers of devices being connected to the Internet. During this same period, service providers’ global network energy consumption has risen by a mere 1.6 times, while enabling around 70% of the global population to use ICT service every single day for everything from remote banking to connecting with their loved ones.
However, we cannot take our eye off the ball. The sobering reality is that the overall energy consumption of ICT continues to increase in absolute terms because of the additional network capacity needed to support the growing digital economy characterized by the exponential rise in network traffic loads and the availability of new applications, which require more computational resources and bandwidth. This is the primary challenge that our industry must overcome through innovation and new technology.
As 5G continues to scale, the ICT industry will play a decisive role in enabling climate action and reducing global emissions. At Ericsson, our approach to breaking the energy curve and enabling a Net Zero future can be broken down into three core elements:
Sustainable network evolution
To run a sustainable network while meeting business and operational targets, taking a holistic view to network evolution planning is crucial. Oftentimes, organizations within a company have different objectives guiding them, so a working process that prioritizes a holistic view of all perspectives is the foundation to breaking the energy curve.
Without a holistic view, organizations can miss out on key energy-saving and emission reduction opportunities. For example, the bar graph below shows the distribution of energy consumption across the components of both 4G and 5G mobile networks.
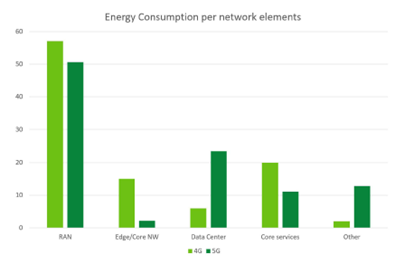
The graph shows that although RAN power consumption has declined in 5G, it still represents over 50% of the total consumption. Another trend is the rise in data center power consumption in 5G as more services/functions move to the cloud. There have been a lot of improvements in energy efficiency and tech advances that allow us to communicate more data using less power. For example, In 5G, spectrum efficiency (i.e. the information rate per cell over a given bandwidth) has improved by an astounding 200% compared to 4G[1]. This is key to preventing energy consumption from growing at the same rate as traffic. However, as the world continues its digital transformation by integrating ICT into all aspects of human activity, we must adopt a holistic approach for securing network energy and sustainability performance for 6G systems.
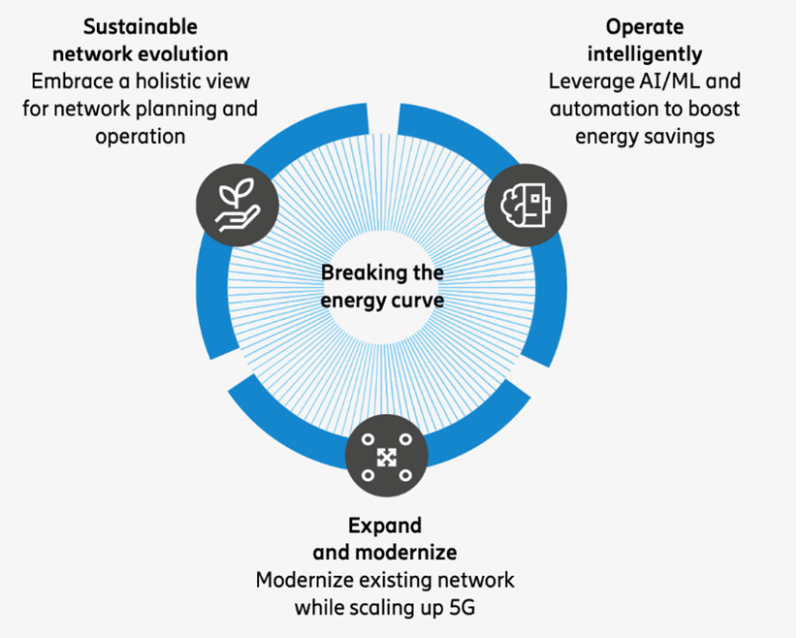
Expand and modernize
To reduce energy consumption when scaling up 5G, modernizing existing equipment is vital. Network modernization is very important for minimizing energy consumption in the immediate future. As noted in the Green G white paper, some estimates claim that modernizing from 4G to 5G RAN hardware could save as much as 90% of the energy needed per bit communicated.
Installing the right equipment at the right place can help reduce both CAPEX and OPEX.
Operate intelligently
Traffic varies on a daily basis, which means the use of energy-saving functionality is essential to adjusting the capacity of mobile networks to match demand and to deliver the best user experience with the lowest energy use. Leveraging AI and machine learning automation can allow for maximized traffic performance for deployed hardware with minimized energy use.
Deploying software solutions that enable energy savings with enhancements to sleep mode functionality can further reduce power consumption. It is also important to build sites with precision. Finally, we must leverage AL/ML technologies to operate site infrastructure more proactively, helping reduce operation and maintenance costs and associated emissions.
Looking ahead
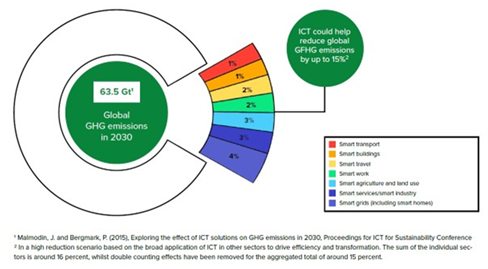
To meet the goal of the Paris climate agreement, we need to cut emissions by 50% by 2030 and drive an additional 50% reduction each decade to reach Net Zero latest by 2050. Digitalization can enable up to 15% reduction in global GHG emissions by 2030. Further reductions will rely on carbon reductions in the ICT sector and improving the potential of 5G networks to enable decarbonization.
Although the ICT industry only accounts for 1.4% of global emissions, it has the potential to enable a 15% reduction of overall global emissions this decade by enabling decarbonization of key economic sectors.
In the long term the goal is to reach net-zero. From 2030 onwards, deployment of 6G and future generations of communication and computing systems at scale will further improve energy efficiency and sustainability. For our part, Ericsson has set an ambition to be Net Zero across our value chain by 2040, and will work to reduce supply chain and portfolio in use emissions 50% by 2030.
Ericsson is deeply committed to identifying and understanding all the ways we can minimize climate impacts and enable decarbonization of key industries like transportation, manufacturing, energy and agriculture. And as we head into the future, industry initiatives like the Green G working group are essential to meeting sustainability goals.
Technology, innovation and cross-industry collaboration are all going to be essential to our collective ability to make the transformational changes required to address the climate crisis. To succeed in playing our part, the ICT industry must continue to work together to ensure that both 5G and 6G leverage the most energy-efficient technologies possible.
Links:
Ericsson 6G Blog from US perspective - https://www.ericsson.com/en/blog/2022/2/the-long-winding-road-to-6g
Ericsson 6G Vision - https://www.ericsson.com/4927de/assets/local/reports-papers/white-papers/6g--connecting-a-cyber-physical-world.pdf
Next G Webinar: https://nextgalliance.org/videos/the-path-toward-sustainable-6g/