Broadband usage in the U.S. continues to surge as more consumers embrace heavy data consumption.
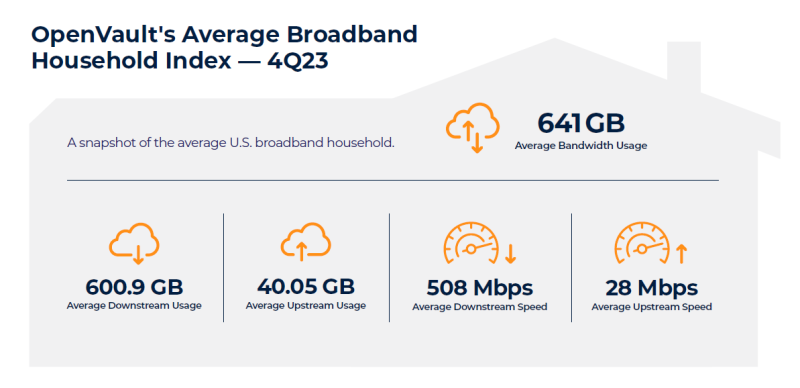
According to a fresh report from OpenVault, the average monthly consumption has more than doubled over the past five years, soaring from 270 GB in 2018 to 641 GB in the fourth quarter of 2023. This marks a 9.3% increase from the previous year's average of 586.7 GB, and the U.S. average is now projected by OpenVault to reach or surpass 700 GB by the close of 2024.
As internet service providers increasingly offer faster speed tiers, about one-third of subscribers are now provisioned for gigabit speeds, a 29% increase over Q422. Conversely, OpenVault found the number of subscribers on speeds below 100 Mbps has dwindled to 10%, a significant decrease (77%) from four years ago.
Despite being on slower speed tiers, 10% of subscribers still on those megabit plans are classified as "power users," a term coined by OpenVault over a decade ago for customers consuming 250 GB or more per month. However, that definition has evolved, now describing consumers using 1 TB or more of data monthly.
The report’s “super power users” category, which consumes 2 TB or more per month, increased by 37% since Q4 2022. And in a new category OpenVault introduced last year, “extreme power users,” those who consume 5 TB or more per month, increased by 71% since then.
Extreme power users consume, on average, 6.6 TB of downstream and nearly 1 TB of upstream data. That’s seven times more downstream and 15 times more upstream data compared to users that consume less than 1 TB monthly.
Power users comprise 38% of all consumers provisioned for gigabit speed. But around 15% of “extreme power users” are provisioned at speeds under 200 Mbps. Those using high amounts of data, but still on megabit tiers, “would significantly improve their online experience by upgrading to a faster speed plan," said OpenVault.
Commercial market does the heavy lifting
The OpenVault report highlighted a substantial increase in overall upstream usage, driven largely by the commercial market, which has seen a 153.48% growth over five years, to 40.05 GB.
Commercial subscribers, on average, used over 70% more upstream data than residential users, with monthly usage reaching 68 GB compared to residential users' 39 GB. Factors contributing to this difference included businesses' reliance on data-intensive activities like file transfers, video calls and cloud-based applications.
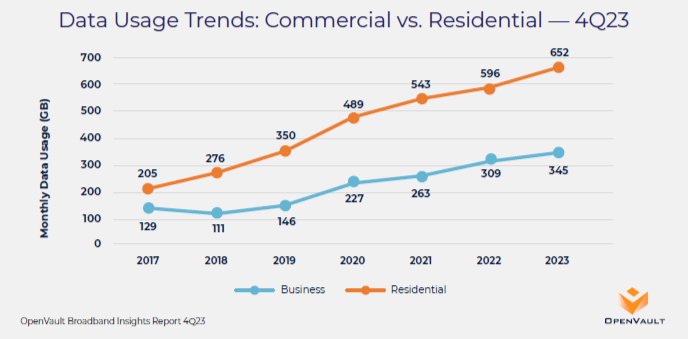
The shift to remote work during the pandemic further widened the gap in data usage between commercial and residential subscribers, as many business-specific activities occurred on residential internet plans. While average hourly usage between the two groups was similar during typical business hours, the disparity increased during evening hours as residential activities like streaming and gaming peaked.
Customer satisfaction hinges on QoE
Growing levels of usage pose significant challenges for network performance, increasing the risk of congestion and dissatisfaction among subscribers.
OpenVault cited Pivot Group customer satisfaction surveys that showed at least 40% of rural broadband customers say improvements to speed, speed consistency and/or connection reliability would have the greatest positive impact on their satisfaction. Most even said they might pay extra for those performance enhancements.
However, internet speed alone is no longer the sole competitive advantage, as customers increasingly prioritize consistency and reliability, OpenVault warned. “Surges in data usage demand will continue to impact network performance, which profoundly influences the customer experience,” its report said.
Rural broadband customers, in particular, highlight the importance of speed improvements and reliability enhancements. Quality of Experience (QoE) issues often stem from network issues, such as overuse by a single user or physical impairments like weather or broken connections, according to OpenVault.
With these challenges and the adoption of advanced network technologies like DOCSIS 3.1 and DOCSIS 4.0, tools like Profile Management Application (PMA) and Proactive Network Maintenance (PNM) are becoming essential for optimizing both network performance and subscriber experiences.
